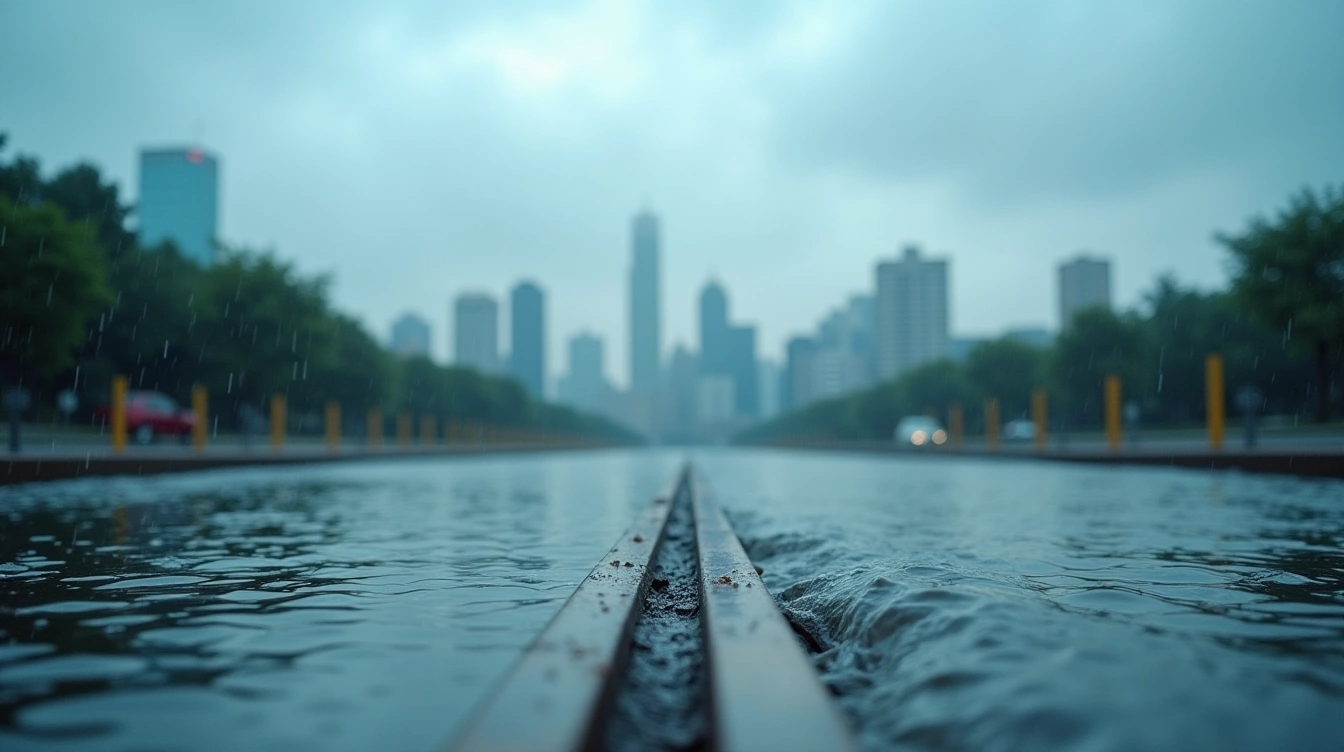
Floods remain among the most costly and disruptive natural disasters globally, affecting millions each year. As climate patterns shift and urbanization accelerates, communities must rethink their approach to flood prevention and management. Recent advancements—both technological and nature-based—have ushered in a new era of innovation aimed at limiting flooding and its destructive impacts. Exploring these approaches reveals practical methods that blend engineering ingenuity with environmental sensitivity.
The evolving landscape of stormwater management
Urban development frequently disrupts the natural flow of water, making stormwater management a crucial aspect of modern city planning. Traditional drainage systems often prove inadequate during heavy rainfall, prompting engineers and planners to combine advanced technology with sustainable design. Managing runoff efficiently not only reduces pressure on sewer systems but also helps prevent dangerous flash floods.
Also read : Innovative oil pipeline solutions for today’s energy challenges
Cities are increasingly deploying adaptive infrastructure that responds intelligently to changing weather conditions. Solutions range from upgraded storm drains to large underground reservoirs, which temporarily store excess water before releasing it gradually. By integrating established techniques with innovative stormwater management systems, communities strengthen their ability to withstand severe weather events and minimize catastrophic damage.
Harnessing technology: ai-powered flood forecasting and early warning systems

Digital tools now play a pivotal role in flood preparedness. Advances in computing allow experts to predict localized flooding with unprecedented precision. Ai-powered flood forecasting uses vast datasets—including weather, topography, and historical records—to generate real-time predictions that help authorities and residents take timely action.
Also to read : Revolutionizing customer experience: how chatbots are transforming service for retailers in the uk
These insights feed directly into advanced early warning systems. Smart sensors continuously monitor stream heights, soil saturation, and rainfall, transmitting data to forecasting models. When risks reach critical levels, alerts are distributed through mobile phones, sirens, and community networks. Key components include:
- 🤖 Real-time monitoring stations
- 📱 Automated public alert networks
- 🌐 Remote sensor data collection
- 📊 Predictive dashboards for decision-makers
Together, these technologies enhance readiness at both individual and municipal levels, potentially saving lives and reducing property loss. In addition, the implementation of modular flood barriers for properties is gaining popularity as a highly effective means to safeguard buildings against rising water.
Nature-based solutions: green and natural infrastructure
Relying solely on concrete barriers and pumps overlooks the essential contribution of healthy ecosystems in flood mitigation. Green infrastructure leverages natural landscapes to absorb, slow, and filter stormwater, increasing resilience while improving urban livability.
What defines green infrastructure and how does it help?
Green infrastructure incorporates vegetation, soils, and natural processes to manage water and foster healthier environments. Features such as rain gardens, grass swales, tree canopies, and constructed wetlands channel and filter rainwater. Strategically placed, they break up hard surfaces that would otherwise accelerate runoff.
Permeable pavement further reduces surface water buildup by allowing rainfall to seep into the subsoil, replenishing groundwater instead of overwhelming drainage networks. Collectively, these solutions deliver multiple benefits including increased biodiversity and cooler city temperatures, alongside effective flood risk reduction.
Restoring natural infrastructure for community protection
Natural infrastructure refers to preserving or restoring habitats like wetlands, riverbanks, and forested floodplains. These areas act as living sponges during storms—absorbing significant amounts of water, slowing its movement, and limiting erosion. Communities that invest in wetland rehabilitation often achieve more reliable long-term flood control than those relying solely on engineered defenses.
Moreover, integrating parks and public spaces designed to serve as temporary flood zones allows water to recede naturally, easing peak flows when it matters most. Such initiatives typically require less maintenance over time and may benefit from conservation funding.
Physical adaptations: flood barriers, floating homes, and resilient building designs
Engineers have responded to unpredictable weather with creative construction strategies. Physical interventions span a wide range—from moveable levees to innovative housing concepts—addressing immediate needs while anticipating future challenges.
Leveraging flood barriers and control systems
Flood barriers and control systems prevent water from overtopping banks or entering vulnerable zones. Available options include inflatable flood walls, retractable gates, and modular blocks that can be deployed quickly when needed. Some municipalities automate these systems, activating them only when sensors predict flooding, thus minimizing disruption and maintenance outside emergencies.
Well-designed flood barrier systems provide layered defense around vital infrastructure, neighborhoods, and business districts, ensuring economic activity continues even if surrounding areas face inundation. For comparison:
| 🛡️ System type | ⚙️ Deployment speed | 💧 Water resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Inflatable barriers | Fast (hours) | Moderate |
| Retractable gates | Automatic/Manual | High |
| Modular blocks | Rapid assembly | Medium |
Housing solutions: floating homes and flood proof structures
Communities prone to frequent flooding are embracing floating homes inspired by amphibious architecture. These houses adapt to rising water by lifting above the floodplain, significantly reducing damage and post-disaster displacement. Floating residences combine buoyant foundations with robust superstructures for added safety.
Conversely, flood proof and resistant structures employ durable materials and elevated designs to minimize water intrusion. Techniques include raising buildings on pilings, applying waterproof coatings, and reinforcing ground-level walls. In high-risk areas, building codes increasingly require these features to better protect residents and assets.
Integrating innovations for holistic flood mitigation
No single solution can address every scenario related to flood risk. Effectiveness rises dramatically when diverse innovations operate together. Forward-thinking cities often implement comprehensive strategies such as:
- 🌳 Widespread use of rain gardens and permeable pavement to encourage infiltration and intercept runoff at the source
- 🔬 Real-time data from ai-powered flood forecasting and early warning systems to maximize response lead time
- 🏡 Residential clusters built to floating or flood-resistant standards tailored to local hazards
- 🚧 Automated flood barriers shielding essential commercial centers and evacuation routes
Integrated planning that unites infrastructure upgrades, ecological restoration, advanced analytics, and community engagement delivers lasting improvements. This synergy limits the financial, social, and environmental costs of flooding across varied geographic regions.
Essential questions about limiting flood impacts
How does green infrastructure reduce urban flooding?
Green infrastructure employs natural elements—such as plants, soils, and wetlands—to manage stormwater in urban settings. Vegetated features capture and slow rainwater runoff, promoting absorption and filtering pollutants before they reach waterways. Common examples include:
- 🌱 Rain gardens capturing water from roofs and driveways
- 🌿 Tree plantings intercepting rainfall and stabilizing soil
- 🌀 Permeable pavement enabling water to soak into the ground
What are the main advantages of ai-powered flood forecasting?
Ai-powered flood forecasting provides precise, location-specific predictions by analyzing extensive datasets far faster than manual methods. Authorities receive earlier warnings and targeted recommendations, resulting in fewer casualties and reduced recovery costs. Notable advantages include:
- ⏰ Faster reaction times
- 📈 Greater accuracy in predicting small-area flood events
- 🔔 Seamless integration with early warning systems
What is the difference between flood proof and flood resistant structures?
Flood proof structures aim to block water entry entirely using watertight barriers, sealed walls, or mechanical pumps. Flood resistant structures accept that some water may enter but use raised foundations and moisture-tolerant materials for quick recovery and minimal damage. Key differences include:
| 🏠 Design element | 🔒 Flood proof | ⚡ Flood resistant |
|---|---|---|
| Entry points | Sealed | Allowable but controlled |
| Materials | Impervious | Water-tolerant |
| Elevation | Optional | Typically elevated |
Why are floating homes seen as a viable solution in flood-prone zones?
Floating homes automatically adjust to water levels, avoiding the structural damage common to conventional dwellings during floods. They offer residents improved safety and peace of mind, especially where land-based mitigation options are limited. Typical features include:
- ⚓ Buoyant platforms for vertical mobility
- 🏗️ Anchoring mechanisms to prevent drifting
- 🚪 Elevated access points for secure entry